SOFTWAREFORMAZIONECONSULENZA
SULLA SOSTENIBILITÀ
Double Materiality Analysis
GPP provides you with all the data you need.

Double Materiality in the CSRD: A Strategic Guide for Businesses
Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD) introduces the innovative concept of double materiality. This requires companies not only to report on relevant material topics but also to analyze how these impact financial results and external effects on the environment and society. In the past, businesses focused on traditional materiality, primarily addressing ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) topics relevant to the organization. With the introduction of the CSRD, the analysis expands, requiring a broader assessment that also considers the external effects on the company’s economic outcomes.
Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD) introduces the innovative concept of double materiality. This requires companies not only to report on relevant material topics but also to analyze how these impact financial results and external effects on the environment and society. In the past, businesses focused on traditional materiality, primarily addressing ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) topics relevant to the organization. With the introduction of the CSRD, the analysis expands, requiring a broader assessment that also considers the external effects on the company’s economic outcomes.
GPP
Tools
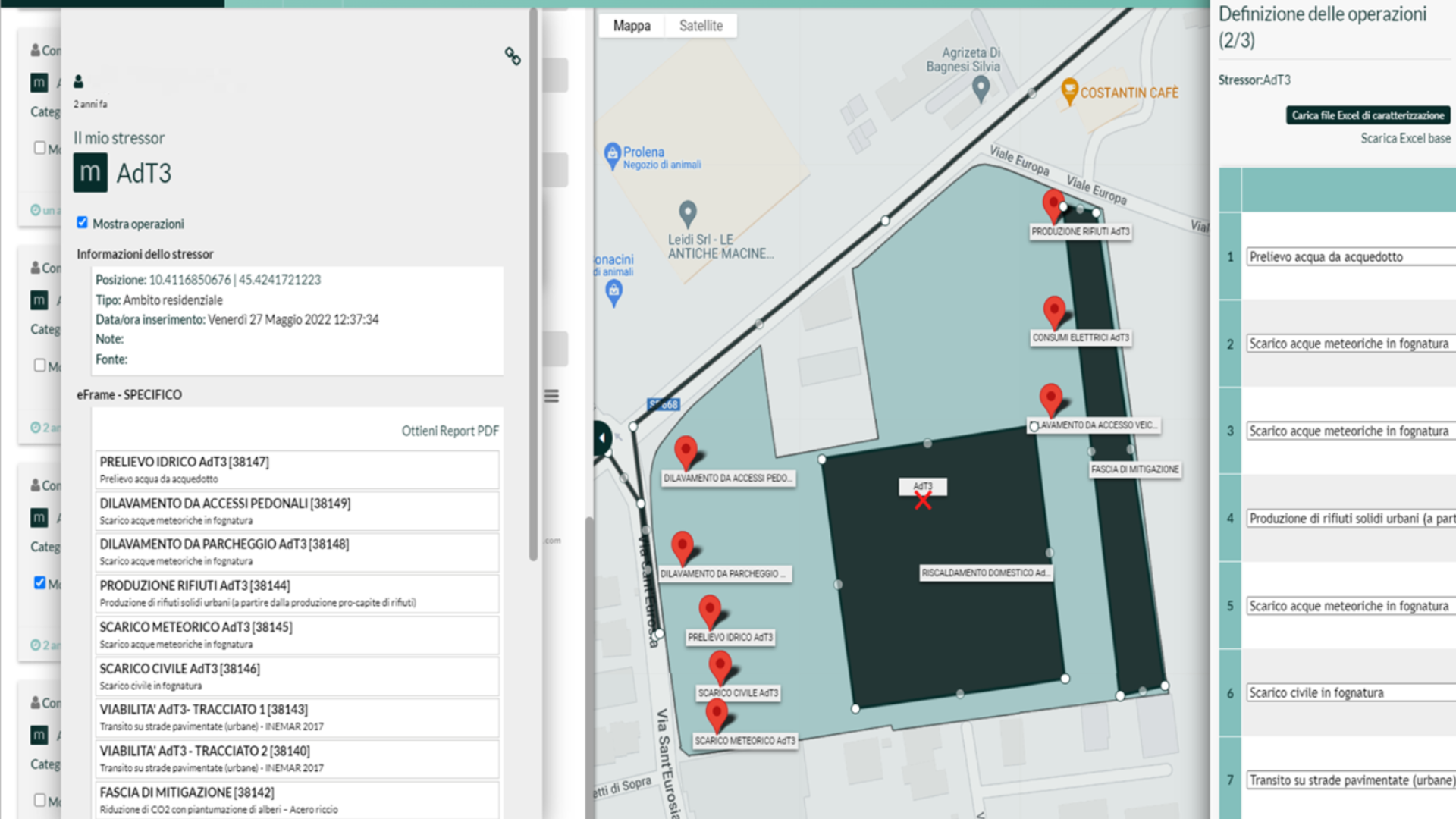
Project/plan characterization tool
Multi-benchmark tool for quantifying and assessing environmental impacts and risks of a company
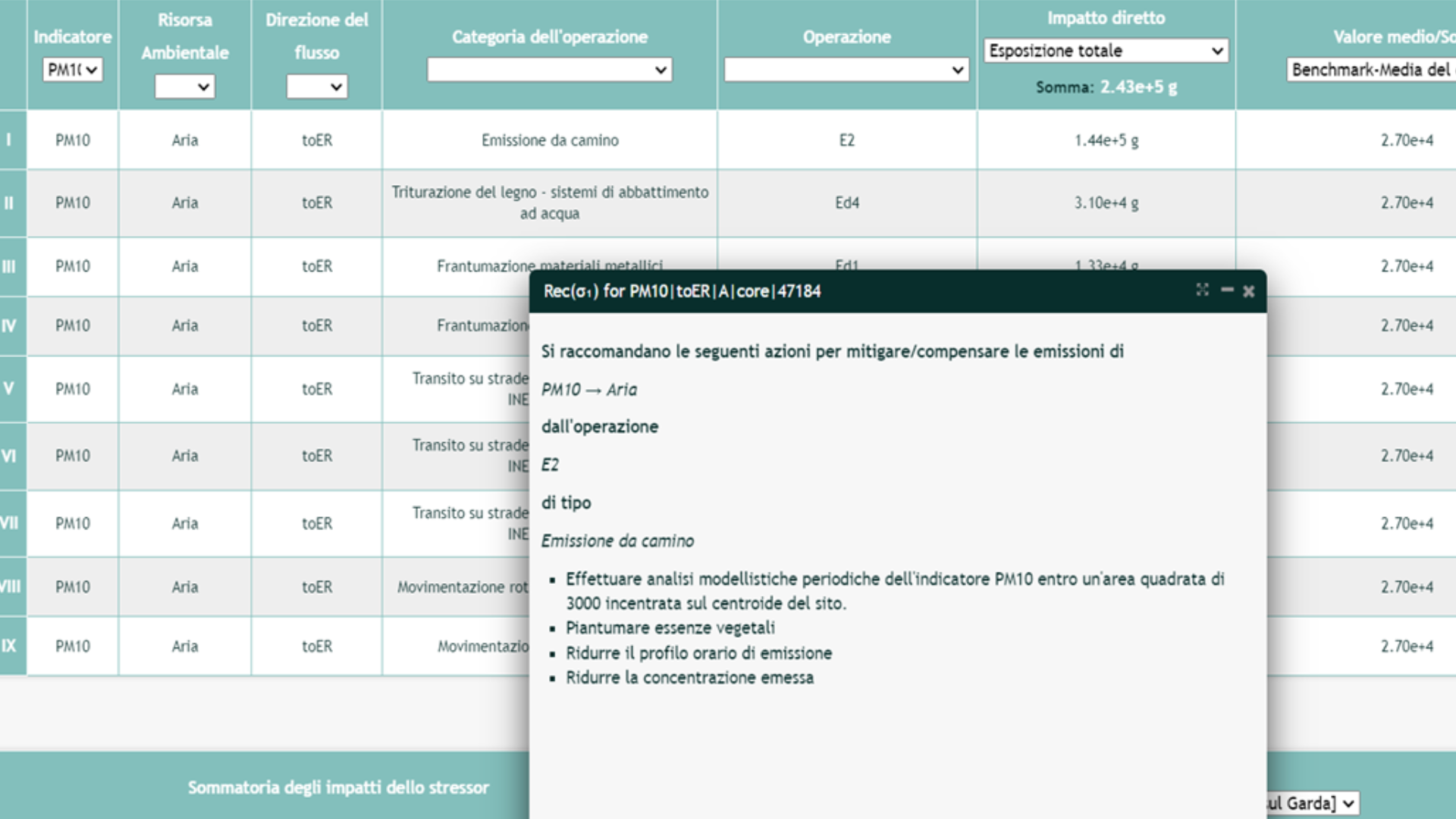
Tool for identifying recommendations to improve impact performance
Tool di quantificazione delle degli impatti indiretti – Analisi delle ricadute
Corporate georeport
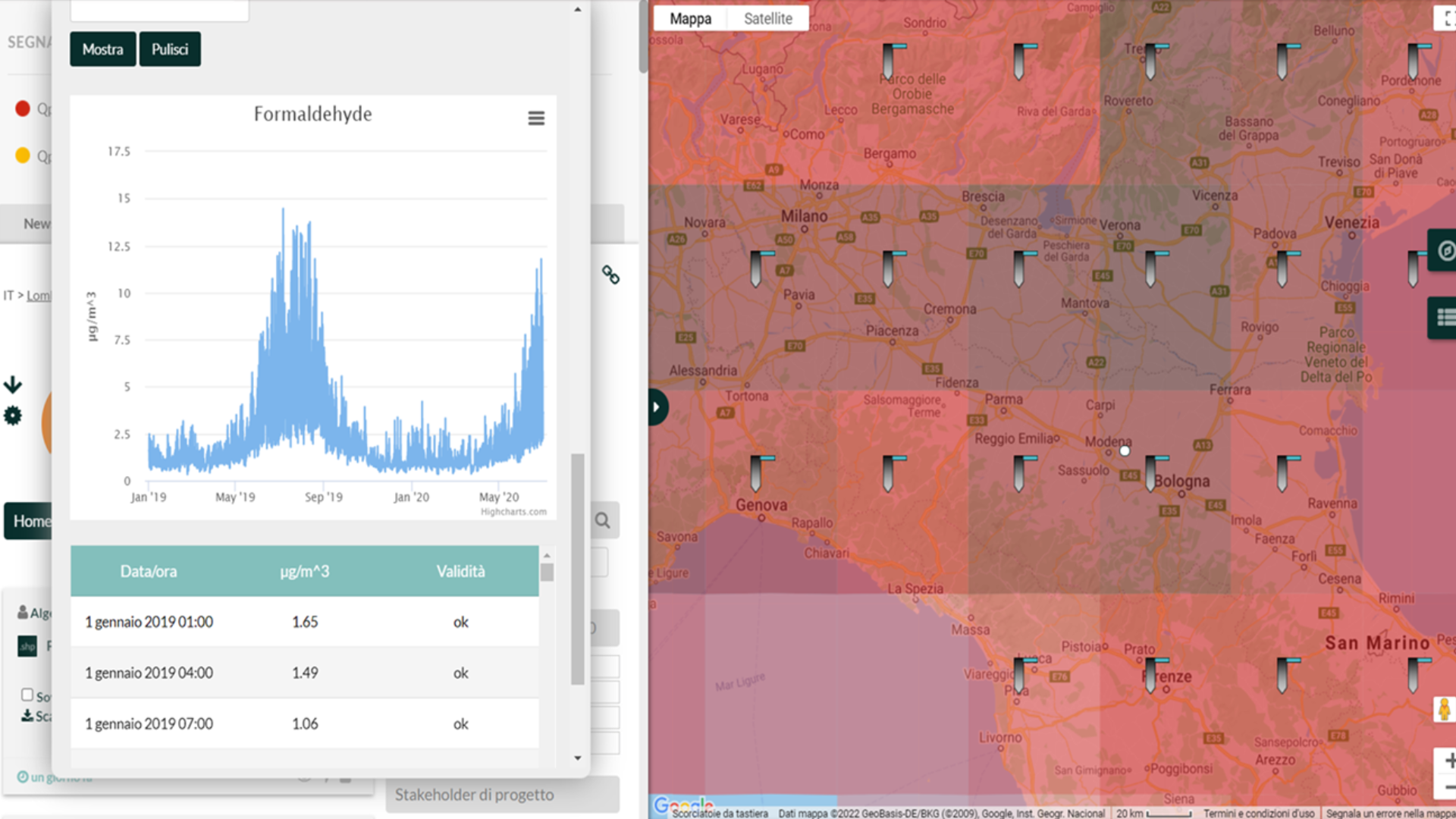
Dynamic tool for monitoring air quality
Territorial georeport
Territorial scoremap
Tool for analyzing double materiality in a territorial context
Basic information framework (stressors and vulnerabilities)
The approval of Legislative Decree No. 125 of September 6, 2024, which transposes the European CSRD Directive (Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive), marks a significant turning point for Italian businesses. This new regulation extends sustainability reporting obligations not only to large companies but also to listed small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs), pushing the entire business sector towards greater environmental, social, and governance (ESG) transparency.
Sustainability Manager
The approval of Legislative Decree No. 125 of September 6, 2024, which transposes the European CSRD Directive (Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive), marks a significant turning point for Italian businesses. This new regulation extends sustainability reporting obligations not only to large companies but also to listed small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs), pushing the entire business sector towards greater environmental, social, and governance (ESG) transparency.
Benefits
Key Features of GREEN PATH PILOT
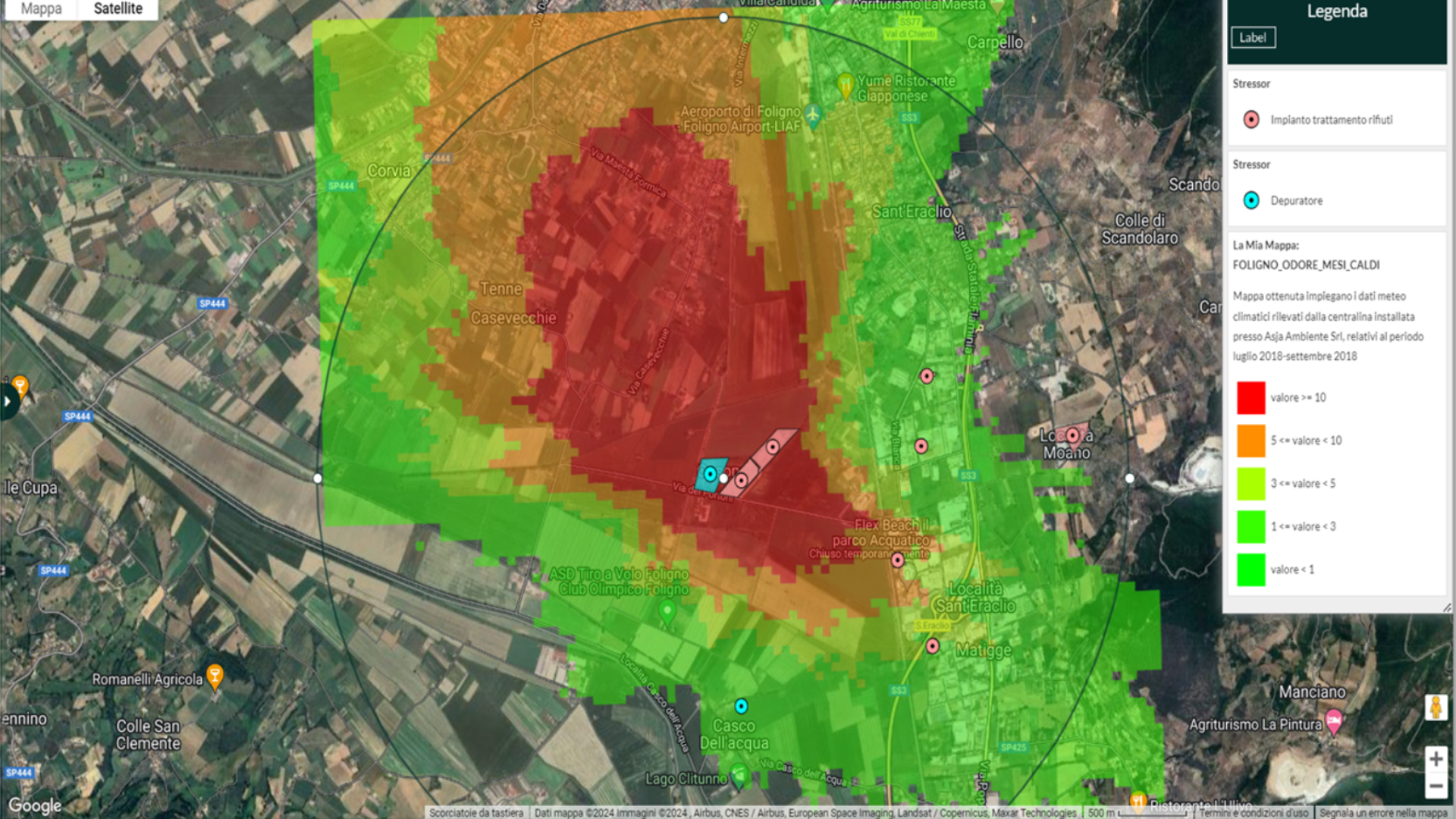
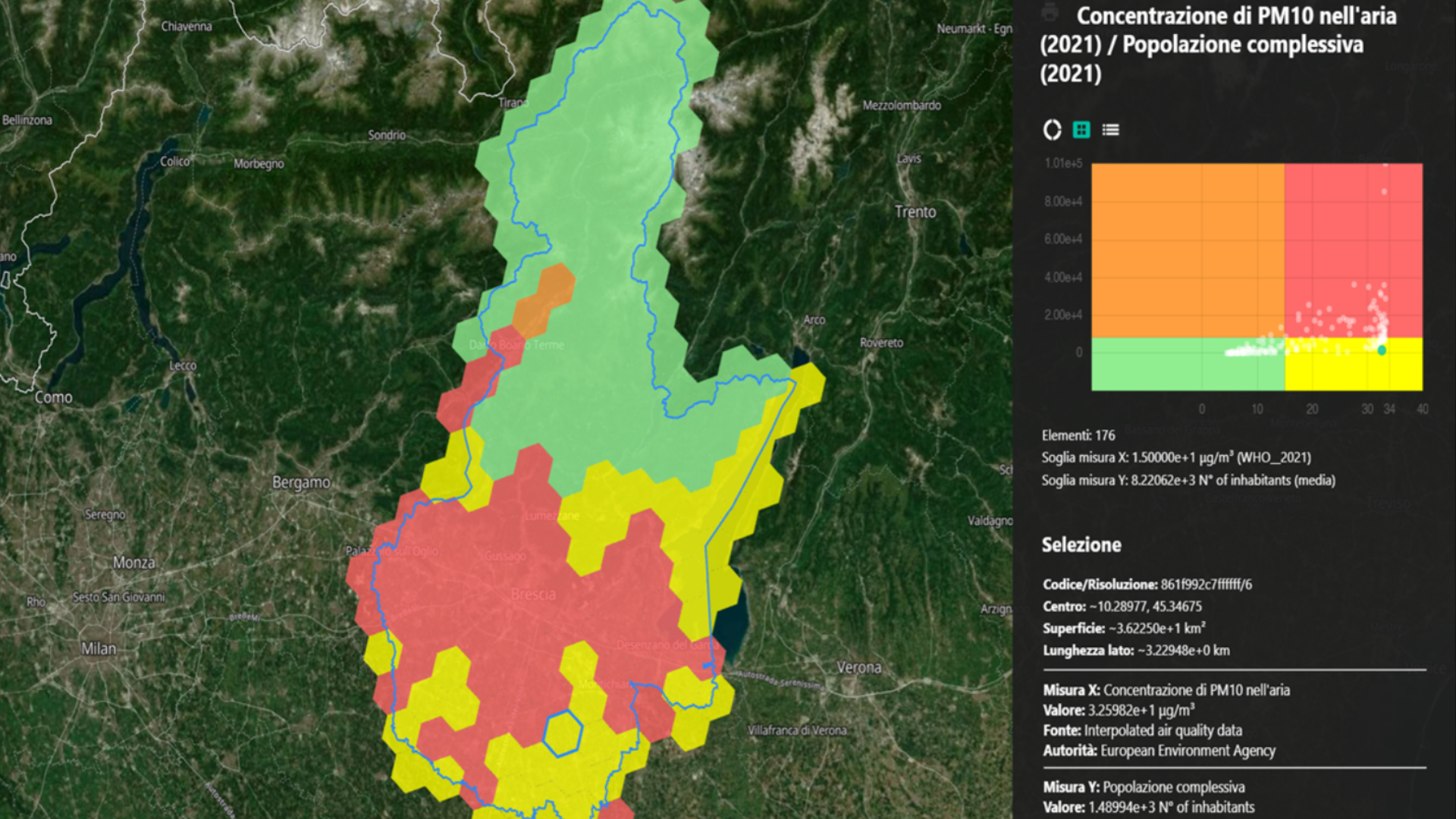
Thanks to the use of satellite data and a network of sensors distributed across the territory, GREEN PATH PILOT enables the association of a specific geographic location with certain pollution levels. In other words, for each individual GPS position, the platform can provide precise data on environmental conditions, allowing for an accurate mapping of high-risk areas.
One of the platform's most advanced features is its ability to identify specific sources of pollution, such as industrial plants, vehicular traffic, landfills, or other potentially polluting activities. This functionality allows users to precisely understand which sources are causing a negative impact on a given area.
GREEN PATH PILOT collects and integrates data from public entities, research institutes, and other reliable sources, ensuring the quality and reliability of the information. Environmental data is validated and made available to users through an intuitive dashboard, providing a clear and interactive visualization of the information.
Thanks to the use of satellite data and a network of sensors distributed across the territory, GREEN PATH PILOT enables the association of a specific geographic location with certain pollution levels. In other words, for each individual GPS position, the platform can provide precise data on environmental conditions, allowing for an accurate mapping of high-risk areas.
ESG Regulations
Legislative Decree 125/2024: New Sustainability Reporting Obligations for Italian Companies
The Italian regulatory landscape on corporate sustainability has undergone a significant evolution with the entry into force of Legislative Decree No. 125 of September 6, 2024. This decree, which transposes Directive (EU) 2464/2022 on Corporate Sustainability Reporting (Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive - CSRD), replaces the previous Legislative Decree No. 254/2016 concerning the declaration of non-financial information (NFRD). The new provisions introduce stricter and more detailed obligations for companies, aiming to enhance transparency and reliability in the sustainability information communicated to the market.
Legislative Decree 125/2024: New Sustainability Reporting Obligations for Italian Companies
The Italian regulatory landscape on corporate sustainability has undergone a significant evolution with the entry into force of Legislative Decree No. 125 of September 6, 2024. This decree, which transposes Directive (EU) 2464/2022 on Corporate Sustainability Reporting (Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive - CSRD), replaces the previous Legislative Decree No. 254/2016 concerning the declaration of non-financial information (NFRD). The new provisions introduce stricter and more detailed obligations for companies, aiming to enhance transparency and reliability in the sustainability information communicated to the market.
Sustainable Development Goals
AGENDA 2030
Goal 1: End poverty in all its forms everywhere
1.1 By 2030, eradicate extreme poverty for all people everywhere, currently measured as those living on less than $1.25 per day.
1.2 By 2030, reduce at least by half the proportion of men, women, and children of all ages living in poverty in all its dimensions, according to national definitions.
1.3 Implement nationally appropriate social protection systems and measures for all, including the most vulnerable, and by 2030 achieve substantial coverage of the poor and vulnerable.
1.4 By 2030, ensure that all men and women, particularly the poorest and most vulnerable, have equal rights to economic resources, as well as access to basic services, ownership, control over land and other forms of property, inheritance, natural resources, appropriate new technologies, and financial services, including microfinance.
1.5 By 2030, strengthen the resilience of the poor and those in vulnerable situations and reduce their exposure and vulnerability to extreme climate events, disasters, and economic, social, and environmental shocks.
1.a Ensure adequate mobilization of resources from various sources, including through development cooperation, to provide reliable and sufficient means for developing countries, particularly least developed countries, to implement programs and policies to end poverty in all its forms.
1.b Create strong policy systems at the national, regional, and international levels, based on development strategies that prioritize the poor and are gender-sensitive, to support accelerated investments in poverty alleviation actions.
Goal 2: End hunger, achieve food security, improve nutrition, and promote sustainable agriculture
2.1 By 2030, end hunger and ensure access to safe, nutritious, and sufficient food for all people, particularly the poor and the most vulnerable, including infants, year-round.
2.2 By 2030, end all forms of malnutrition; achieve internationally agreed targets by 2025 to address stunting and wasting in children under 5 years of age; meet the nutritional needs of adolescent girls, pregnant and lactating women, and older persons.
2.3 By 2030, double agricultural productivity and the income of small-scale food producers, particularly women, indigenous peoples, farming families, pastoralists, and fishers, including through secure and equitable access to land, other resources and productive inputs, knowledge, financial services, markets, and opportunities for value-added and non-agricultural employment.
2.4 By 2030, ensure sustainable food production systems and implement resilient agricultural practices that increase productivity and production, help protect ecosystems, strengthen the ability to adapt to climate change, extreme weather, droughts, floods, and other disasters, and progressively improve soil quality.
2.5 By 2020, maintain the genetic diversity of seeds, cultivated plants, farmed and domesticated animals, and related wild species, including through diversified and properly managed seed banks and plant collections at the national, regional, and international levels; promote access to and the fair and equitable sharing of benefits arising from the use of genetic resources and associated traditional knowledge, as agreed upon at the international level.
2.a Increase investments, including through enhanced international cooperation, in rural infrastructure, agricultural research and training, technological development, and plant and animal gene banks, to improve agricultural productivity in developing countries, particularly least developed countries.
2.b Correct and prevent trade restrictions and distortions in global agricultural markets, including through the parallel elimination of all forms of agricultural export subsidies and all export measures with equivalent effect, in accordance with the mandate of the Doha Development Round.
2.c Adopt measures to ensure the proper functioning of food commodity markets and their derivatives and facilitate quick access to market information, including food reserves, in order to help limit extreme food price volatility.
Goal 3: Ensure health and well-being for all at all ages
3.1 By 2030, reduce the global maternal mortality ratio to less than 70 per 100,000 live births.
3.2 By 2030, end preventable deaths of newborns and children under 5 years of age. All countries should aim to reduce neonatal mortality to at least 12 per 1,000 live births and under-5 mortality to at least 25 per 1,000 live births.
3.3 By 2030, end the epidemics of AIDS, tuberculosis, malaria, and neglected tropical diseases; combat hepatitis, waterborne diseases, and other communicable diseases.
3.4 By 2030, reduce by one-third premature mortality from non-communicable diseases through prevention and treatment and promote well-being and mental health.
3.5 Strengthen the prevention and treatment of substance abuse, including drug abuse and harmful alcohol consumption.
3.6 By 2020, halve the global number of deaths and injuries from road traffic accidents.
3.7 By 2030, ensure universal access to sexual and reproductive health care services, including family planning, information, education, and the integration of reproductive health into national strategies and programs.
3.8 Achieve universal health coverage, including protection from financial risks, access to essential quality health services, and safe, effective, quality, and affordable access to essential medicines and vaccines for all.
3.9 By 2030, substantially reduce the number of deaths and diseases from hazardous chemicals and contamination and pollution of air, water, and soil.
3.a Strengthen the implementation of the World Health Organization Framework Convention on Tobacco Control in all countries, as appropriate.
3.b Support research and development of vaccines and medicines for communicable and non-communicable diseases that primarily affect developing countries; provide access to essential and affordable medicines and vaccines, in accordance with the Doha Declaration on the TRIPS Agreement and Public Health, which affirms the right of developing countries to use the so-called "flexibilities" in intellectual property to protect public health and, in particular, provide access to medicines for all.
3.c Significantly increase health financing and the recruitment, training, development, and retention of the health workforce in developing countries, especially in least developed countries and small island developing states.
3.d Strengthen the capacity of all countries, especially developing countries, to detect, reduce, and manage health risks, both nationally and globally.
Goal 4: Ensure inclusive and equitable quality education and promote lifelong learning opportunities for all
4.1 By 2030, ensure that all girls and boys complete free, equitable, and quality primary and secondary education leading to relevant and effective learning outcomes.
4.2 By 2030, ensure that all girls and boys have access to quality early childhood development, care, and pre-primary education so that they are ready for primary education.
4.3 By 2030, ensure equal access for all women and men to affordable and quality technical, vocational, and tertiary education, including university education.
4.4 By 2030, significantly increase the number of youth and adults with skills, including technical and vocational skills, for employment, decent jobs, and entrepreneurship.
4.5 By 2030, eliminate gender disparities in education and ensure equal access to all levels of education and vocational training for vulnerable groups, including persons with disabilities, indigenous populations, and children in vulnerable situations.
4.6 By 2030, ensure that all youth and a substantial proportion of adults, both men and women, achieve literacy and numeracy skills.
4.7 By 2030, ensure that all learners acquire the knowledge and skills needed to promote sustainable development, including through education aimed at sustainable development and lifestyles, human rights, gender equality, promotion of a culture of peace and non-violence, global citizenship, and appreciation of cultural diversity and culture's contribution to sustainable development.
4.a Build and upgrade education facilities that are child-sensitive, disability-friendly, and gender-sensitive, and provide safe, non-violent, and inclusive learning environments for all.
4.b By 2020, significantly increase the number of scholarships available globally for developing countries, especially in least developed countries, small island developing states, and African countries, to ensure access to higher education—including vocational training, information and communication technologies, and technical, engineering, and scientific programs—both in developed and developing countries.
4.c By 2030, significantly increase the number of qualified teachers, including through international cooperation, for their training activities in developing countries, especially in least developed countries and small island developing states.
Goal 5: Achieve gender equality and empower all women and girls
5.1 End all forms of discrimination against all women and girls everywhere.
5.2 Eliminate all forms of violence against women and girls, both in the public and private spheres, including trafficking of women and sexual exploitation and other types of exploitation.
5.3 Eliminate all harmful practices, such as child marriage, early and forced marriage, and female genital mutilation.
5.4 Recognize and value unpaid care and domestic work, through public services, infrastructure, and social protection policies, and promote shared responsibilities within families, in accordance with national standards.
5.5 Ensure full and effective participation of women and equal opportunities for leadership at all levels of decision-making in political, economic, and public life.
5.6 Ensure universal access to sexual and reproductive health and rights, as agreed in the Programme of Action of the International Conference on Population and Development and the Beijing Platform for Action, along with documents produced in subsequent conferences.
5.a Initiate reforms to give women equal rights to economic resources, as well as ownership and control over land and other forms of property, financial services, inheritance, and natural resources, in accordance with national laws.
5.b Enhance the use of enabling technologies, particularly information and communication technologies, to promote women's empowerment.
5.c Adopt and strengthen sound policies and legislation to promote gender equality and the empowerment of all women and girls at all levels.
Goal 6: Ensure availability and sustainable management of water and sanitation for all
6.1 By 2030, achieve universal and equitable access to safe and affordable drinking water for all.
6.2 By 2030, achieve access to adequate and equitable sanitation and hygiene for all and end open defecation, paying special attention to the needs of women and girls and those in vulnerable situations.
6.3 By 2030, improve water quality by eliminating dumping, reducing pollution, and minimizing the release of hazardous chemicals and materials, halving untreated wastewater, and significantly increasing global recycling and safe reuse.
6.4 By 2030, substantially increase water-use efficiency across all sectors and ensure sustainable withdrawals and supply of freshwater to address water scarcity and significantly reduce the number of people suffering from its impacts.
6.5 By 2030, implement integrated water resources management at all levels, including through transboundary cooperation, as appropriate.
6.6 By 2030, protect and restore water-related ecosystems, including mountains, forests, wetlands, rivers, aquifers, and lakes.
6.a By 2030, expand international cooperation and support to developing countries for water and sanitation-related activities and programs, including water collection, desalination, water efficiency, wastewater treatment, and recycling and reuse technologies.
6.b Support and strengthen the participation of local communities in improving water and sanitation management.
Goal 7: Ensure access to affordable, reliable, sustainable, and modern energy for all
7.1 By 2030, ensure universal access to affordable, reliable, and modern energy services.
7.2 By 2030, significantly increase the share of renewable energy in the total energy consumption.
7.3 By 2030, double the global rate of improvement in energy efficiency.
7.a By 2030, increase international cooperation to facilitate access to research and technologies related to clean energy, including renewable resources, energy efficiency, and advanced and cleaner fossil fuel technologies, and promote investments in energy infrastructure and clean energy technologies.
7.b By 2030, implement infrastructure and improve technologies to provide modern and sustainable energy services, especially in least developed countries, small island developing states, and landlocked developing countries, in accordance with their respective support programs.
Goal 8: Promote sustained, inclusive, and sustainable economic growth, full and productive employment, and decent work for all
8.1 Sostenere la crescita economica pro capite in conformità alle condizioni nazionali, e in particolare una crescita annua almeno del 7% del prodotto interno lordo nei paesi in via di sviluppo
8.2 Achieve higher levels of economic productivity through diversification, technological progress, and innovation, with a focus on high value-added and labor-intensive sectors.
8.3 Promote development-oriented policies that support productive activities, decent job creation, entrepreneurship, creativity and innovation, and encourage the formalization and growth of micro-, small- and medium-sized enterprises, including through access to financial services
8.4 Improve progressively, through 2030, global resource efficiency in consumption and production and endeavour to decouple economic growth from environmental degradation, in accordance with the 10-year framework of programmes on sustainable consumption and production, with developed countries taking the lead
8.5 By 2030, achieve full and productive employment and decent work for all women and men, including for young people and persons with disabilities, and equal pay for work of equal value
8.6 By 2030, reduce the proportion of youth who are unemployed and not in education or training.
8.7 Take immediate and effective measures to eradicate forced labor, end modern slavery and human trafficking, and ensure the prohibition and elimination of the worst forms of child labor, including the recruitment and use of child soldiers, and end child labor in all its forms by 2025.
8.8 Protect labor rights and promote a safe and secure working environment for all workers, including migrants, particularly women, and those in precarious employment.
8.9 Design and implement policies by 2030 to promote sustainable tourism that creates jobs and promotes local culture and products.
8.10 Strengthen the capacity of domestic financial institutions to encourage and expand the use of banking, insurance, and financial services for all.
8.a Increase support for trade-related assistance for developing countries, particularly least developed countries, including through the Enhanced Integrated Framework for technical assistance related to trade for least developed countries.
8.b Develop and operationalize by 2020 a global strategy for youth employment and implement the International Labour Organization’s Global Jobs Pact.
Goal 9: Build resilient infrastructure, promote inclusive and sustainable industrialization, and foster innovation
9.1 Develop quality, reliable, sustainable, and resilient infrastructure, including regional and transboundary infrastructure, to support economic development and human well-being, with a particular focus on equitable and affordable access for all.
9.2 Promote inclusive and sustainable industrialization and significantly increase the share of employment in industry and GDP by 2030, in line with national contexts, and double this share in least developed countries.
9.3 Increase access for small industrial and non-industrial enterprises, particularly in developing countries, to financial services, including affordable loans, and integrate them into value chains and markets.
9.4 By 2030, upgrade infrastructure and retrofit industries to make them sustainable, with increased resource-use efficiency and the adoption of cleaner and environmentally sound technologies and industrial processes, ensuring that all countries take action in accordance with their respective capacities.
9.5 Increase scientific research, enhance technological capabilities of the industrial sector in all countries—particularly in developing countries—and encourage innovation. Significantly increase, by 2030, the number of researchers per million people in research and development, as well as the research expenditure—both public and private—and for development.
9.a Facilitate the development of sustainable and resilient infrastructure in developing countries through enhanced financial, technical, and technological support for African countries, least developed countries, landlocked countries, and small island developing states.
9.b Support the development of domestic technology, research, and innovation in developing countries, including ensuring an enabling environmental policy, inter alia, for industrial diversification and value-added products.
9.c Significantly increase access to information and communication technologies and strive to provide least developed countries with affordable and universal internet access by 2020.
Goal 10: Reduce inequality within and among countries
10.1 By 2030, progressively achieve and sustain income growth of the bottom 40% of the population at a rate higher than the national average.
10.2 By 2030, empower and promote the social, economic, and political inclusion of all, irrespective of age, sex, disability, race, ethnicity, origin, religion, economic status, or other.
10.3 Ensure equal opportunities and reduce inequalities in outcomes, including by eliminating discriminatory laws, policies, and practices and promoting appropriate legislation, policies, and actions in this regard.
10.4 Adopt policies, particularly fiscal, wage, and social protection policies, to progressively achieve greater equality.
10.5 Improve the regulation and monitoring of global financial institutions and markets, and strengthen the implementation of these regulations.
10.6 Ensure better representation and voice for developing countries in institutions responsible for global and international economic and financial decision-making, to create more effective, credible, accountable, and legitimate institutions.
10.7 Make migration and mobility of people more orderly, safe, regular, and responsible, including through the implementation of well-managed and planned migration policies.
10.a Implement the principle of special and differential treatment for developing countries, particularly least developed countries, in accordance with the agreements of the World Trade Organization.
10.b Encourage official development assistance and financial flows, including foreign direct investments, to the most in-need countries, particularly least developed countries, African countries, small island developing states, and landlocked developing countries, in accordance with their national plans and programs. 10.c By 2030, reduce remittance transaction costs to less than 3% and eliminate remittance corridors with costs above 5%.
Goal 11: Make cities and human settlements inclusive, safe, resilient, and sustainable
11.1 By 2030, ensure access for all to adequate, safe, and affordable housing and basic services, and upgrade slums.
11.2 By 2030, ensure access for all to safe, affordable, accessible, and sustainable transportation systems, improving road safety, particularly through the enhancement of public transport, with special attention to the needs of the most vulnerable, including women, children, persons with disabilities, and the elderly.
11.3 By 2030, enhance inclusive and sustainable urbanization and the capacity of all countries to plan and manage human settlements that are participatory, integrated, and sustainable.
11.4 Strengthen efforts to protect and safeguard the world’s cultural and natural heritage.
11.5 By 2030, significantly reduce the number of deaths and the number of people affected and substantially decrease direct economic losses relative to global GDP caused by disasters, including those related to water, with special attention to protecting the poor and the most vulnerable. 11.6 By 2030, reduce the per capita environmental impact of cities, with special attention to air quality and the management of urban and other waste.
11.7 By 2030, provide universal access to safe, inclusive, and accessible green and public spaces, particularly for women, children, the elderly, and persons with disabilities.
11.a Strengthen positive economic, social, and environmental links between urban, peri-urban, and rural areas by enhancing national and regional development planning.
11.b By 2020, significantly increase the number of cities and human settlements adopting and implementing integrated policies and plans aimed at inclusion, resource efficiency, climate change mitigation and adaptation, disaster resilience, and promoting and implementing a holistic disaster risk management approach at all levels, in line with the Sendai Framework for Disaster Risk Reduction 2015-2030. 11.c Support least developed countries, including through technical and financial assistance, in building sustainable and resilient buildings using local materials.
Goal 12: Ensure sustainable consumption and production patterns
12.1 Implement the 10-Year Framework of Programmes on Sustainable Consumption and Production, with all countries participating, led by developed countries, but also taking into account the development and capacities of developing countries.
12.2 By 2030, achieve the sustainable management and efficient use of natural resources.
12.3 By 2030, halve per capita global food waste at the retail and consumer levels and reduce food losses along production and supply chains, including post-harvest losses.
12.4 By 2020, achieve the environmentally sound management of chemicals and all wastes throughout their lifecycle, in accordance with internationally agreed frameworks, and significantly reduce their release into air, water, and soil to minimize their negative impact on human health and the environment.
12.5 By 2030, substantially reduce waste generation through prevention, reduction, recycling, and reuse.
12.6 Encourage companies, especially large multinational corporations, to adopt sustainable practices and integrate sustainability information into their annual reports.
12.7 Promote sustainable practices in public procurement, in accordance with national policies and priorities.
12.8 By 2030, ensure that all people, everywhere, have the relevant information and awareness for sustainable development and lifestyles in harmony with nature.
12.a Support developing countries in strengthening their scientific and technological capacities to move towards more sustainable consumption and production patterns.
12.b Develop and implement tools to monitor the impacts of sustainable development for sustainable tourism, which creates jobs and promotes local culture and products.
12.c Rationalize inefficient fossil fuel subsidies that encourage wasteful consumption by eliminating market distortions in accordance with national circumstances, including restructuring tax systems and phasing out harmful subsidies, where they exist, to reflect their environmental impact. Special consideration should be given to the specific needs and conditions of developing countries, minimizing potential negative effects on their development to protect the poor and the most affected communities.
Goal 13: Take urgent action to combat climate change and its impacts
13.1 Strengthen the capacity of all countries to adapt to climate-related hazards and natural disasters.
13.2 Integrate climate change measures into national policies, strategies, and planning.
13.3 Improve education, awareness-raising, and human and institutional capacity on climate change mitigation, adaptation, impact reduction, and early warning.
13.a Fulfill the commitment made by developed countries under the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change, which includes mobilizing $100 billion per year by 2020 from all countries participating in the commitment, to address the needs of developing countries in the context of meaningful mitigation actions and transparency in implementation. Also, make the Green Climate Fund fully operational as soon as possible through its capitalization.
13.b Promote mechanisms to enhance the effective capacity for planning and managing climate change-related interventions in least developed countries, small island developing states, with particular attention to women and youth, as well as local and marginalized communities.
Goal 14: Conserve and sustainably use the oceans, seas, and marine resources for sustainable development
14.1 By 2025, prevent and significantly reduce marine pollution of all kinds, particularly from land-based activities, including marine debris and nutrients.
14.2 By 2020, sustainably manage and protect marine and coastal ecosystems to avoid significant negative impacts, including by strengthening their resilience, and take action for their restoration to achieve healthy and productive oceans.
14.3 Minimize and address the impacts of ocean acidification, including through enhanced scientific cooperation at all levels.
14.4 By 2020, effectively regulate fishing and end overfishing, illegal, unreported, and unregulated fishing, and destructive fishing practices. Implement science-based management plans to restore fish stocks in the shortest time possible, bringing them at least to levels that produce the maximum sustainable yield, as determined by their biological characteristics.
14.5 By 2020, conserve at least 10% of coastal and marine areas, in accordance with national and international law and based on the best available scientific information.
14.6 By 2020, prohibit forms of fishing subsidies that contribute to overcapacity and overfishing, eliminate subsidies that contribute to illegal, unreported, and unregulated fishing, and refrain from reintroducing such subsidies. Recognize that special and differential treatment for developing countries and least developed countries, as appropriate and effective, should be an integral part of the World Trade Organization's negotiations on fishing subsidies.
14.7 By 2030, increase the economic benefits of small island developing states and least developed countries from the sustainable use of marine resources, including through sustainable management of fisheries, aquaculture, and tourism.
14.a Increase scientific knowledge, develop research capacity, and promote the transfer of marine technology, taking into account the criteria and guidelines of the Intergovernmental Oceanographic Commission on Marine Technology Transfer, with the goal of improving ocean health and enhancing the contribution of marine biodiversity to the development of emerging countries, particularly small island developing states and least developed countries.
14.b Provide access for small-scale artisanal fishers to marine resources and markets.
14.c Enhance the conservation and sustainable use of oceans and their resources by implementing international law, as reflected in the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea, which provides the legal framework for the conservation and sustainable use of oceans and their resources, as referenced in paragraph 158 of "The Future We Want."
Goal 15: Protect, restore and promote the sustainable use of terrestrial ecosystems, sustainably manage forests, combat desertification, halt and reverse land degradation, and halt biodiversity loss
15.1 By 2020, ensure the conservation, restoration, and sustainable use of freshwater and terrestrial ecosystems and their services, particularly forests, wetlands, mountains, and drylands, in line with the obligations arising from international agreements.
15.2 By 2020, promote the sustainable management of all types of forests, halt deforestation, restore degraded forests, and significantly increase reforestation and afforestation worldwide.
15.3 By 2030, combat desertification, restore degraded land, including land affected by desertification, drought, and floods, and strive to achieve a land degradation-neutral world.
15.4 By 2030, ensure the conservation of mountain ecosystems, including their biodiversity, to enhance their ability to provide essential benefits for sustainable development.
15.5 Take effective and immediate action to reduce the degradation of natural habitats, halt the destruction of biodiversity, and by 2020, protect endangered species from extinction.
15.6 Promote fair and equitable distribution of the benefits arising from the utilization of genetic resources and promote fair access to such resources, as agreed upon internationally.
15.7 Take action to end poaching and trafficking of protected species of flora and fauna and combat the illegal trade in wildlife.
15.8 By 2020, introduce measures to prevent the introduction of invasive alien species and substantially reduce their impact on terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems, and control or eradicate priority species.
15.9 By 2020, integrate ecosystem and biodiversity principles into national and local development projects, processes, and poverty reduction strategies and reports.
15.a Mobilize and significantly increase financial resources from all sources to preserve and sustainably use biodiversity and ecosystems.
15.b Mobilize significant resources from all sources and at all levels to finance the sustainable management of forests and provide adequate incentives for developing countries to improve forest management, as well as for conservation and reforestation efforts.
15.c Strengthen global support to combat poaching and illegal trafficking of protected species, including by enhancing the capacity of local communities to use sustainable livelihoods.
Goal 16: Promote peaceful and inclusive societies for sustainable development, provide access to justice for all, and build effective, accountable, and inclusive institutions at all levels
16.1 Significantly reduce all forms of violence and related death rates everywhere.
16.2 End abuse, exploitation, trafficking, and all forms of violence and torture against children.
16.3 Promote the rule of law at the national and international levels and ensure equal access to justice for all.
16.4 By 2030, significantly reduce illicit financial flows and arms trafficking, enhance the recovery and return of stolen assets, and combat all forms of organized crime.
16.5 Significantly reduce corruption and abuse of power in all their forms.
16.6 Develop effective, accountable, and transparent institutions at all levels.
16.7 Ensure responsive, inclusive, participatory, and representative decision-making at all levels.
16.8 Broaden and strengthen the participation of developing countries in global governance institutions.
16.9 By 2030, provide legal identity for all, including birth registration.
16.10 Ensure public access to information and protect fundamental freedoms, in accordance with national legislation and international agreements.
16.a Strengthen national institutions, including through international cooperation, to develop capacity at all levels, particularly in developing countries, to prevent violence and combat terrorism and crime.
16.b Promote and enforce non-discriminatory laws and sustainable development policies.
Goal 17: Strengthen the means of implementation and revitalize the global partnership for sustainable development
17.2 Developed countries should fulfill their official development assistance commitments, including the target of allocating 0.7% of Gross National Income (GNI) for Official Development Assistance (ODA) to developing countries, and allocate between 0.15% and 0.20% of GNI for ODA to least developed countries; global ODA providers are encouraged to allocate at least 0.20% of GNI to least developed countries.
17.3 Mobilize additional financial resources for developing countries from multiple sources.
17.4 Assist developing countries in sustaining long-term debt through coordinated policies aimed at stimulating financing, debt reduction, and restructuring, and addressing the external debt of the poorest and most heavily indebted countries to reduce their burden.
17.5 Adopt and implement investment promotion regimes for least developed countries.
17.6 Strengthen North-South, South-South, and triangular regional and international cooperation, as well as access to scientific discoveries, technology, and innovations, and improve knowledge sharing based on agreed modalities through greater coordination between existing mechanisms, particularly at the United Nations level, and through a global technology access mechanism.
17.7 Promote the growth, exchange, and dissemination of environmentally friendly technologies in developing countries on favorable terms, through concessional and preferential agreements established by mutual consent.
17.8 By 2017, make operational the mechanism to strengthen the technology bank and science, technology, and innovation for least industrialized countries, and enhance the use of advanced technology, particularly in information and communication technologies.
Development Capacity
17.9 Increase international support to implement effective and targeted capacity development in non-industrialized countries to support national plans for achieving all Sustainable Development Goals, through North-South, South-South, and triangular cooperation.
Trade
17.10 Promote a universal, rules-based, open, non-discriminatory, and multilateral trading system under the World Trade Organization, through negotiations under the Doha Development Agenda.
17.11 Significantly increase the exports of developing countries and, by 2020, double their share of global exports.
17.12 Ensure timely access to markets for least developed countries free of tariffs and quotas on a durable basis, in line with decisions made by the World Trade Organization, ensuring that preferential rules applicable to imports from least developed countries are simple, transparent, and contribute to facilitating market access.
Systemic Issues
Policy and Institutional Coherence
17.13 Promote global macroeconomic stability through policy coordination and coherence.
17.14 Enhance policy coherence for sustainable development.
17.15 Respect the political space and leadership of each country to establish and implement policies for poverty eradication and sustainable development.
Multilateral Cooperation Programs
17.16 Strengthen the global partnership for sustainable development, supported by multilateral collaborations that develop and share knowledge, expertise, technological and financial resources, to achieve the Sustainable Development Goals in all countries, especially in emerging countries.
17.17 Encourage and promote effective partnerships in the public sector, between public and private sectors, and in civil society, based on the experience of partnerships and their ability to mobilize resources.
Data, Monitoring, and Accountability
17.18 By 2020, strengthen support for the development of emerging countries, least developed countries, and small island developing states (SIDS). Increase the availability of high-quality, timely, and reliable data beyond profit, gender, age, race, ethnicity, migration status, disability, geographic location, and other relevant characteristics within the national context.
17.19 By 2030, build on existing initiatives to develop progress measures for sustainable development that complement Gross Domestic Product (GDP), and support the development capacity of emerging countries.